Metal-Organic Frameworks
What are MOFs?
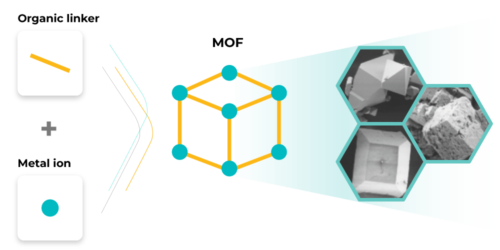
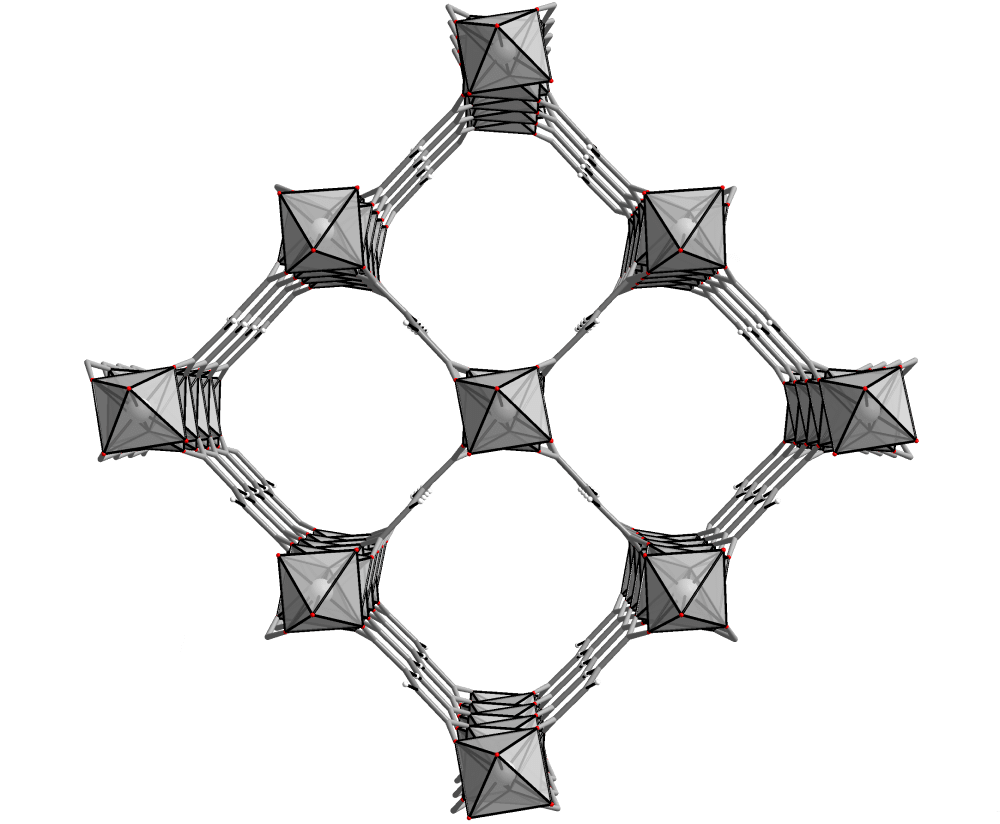
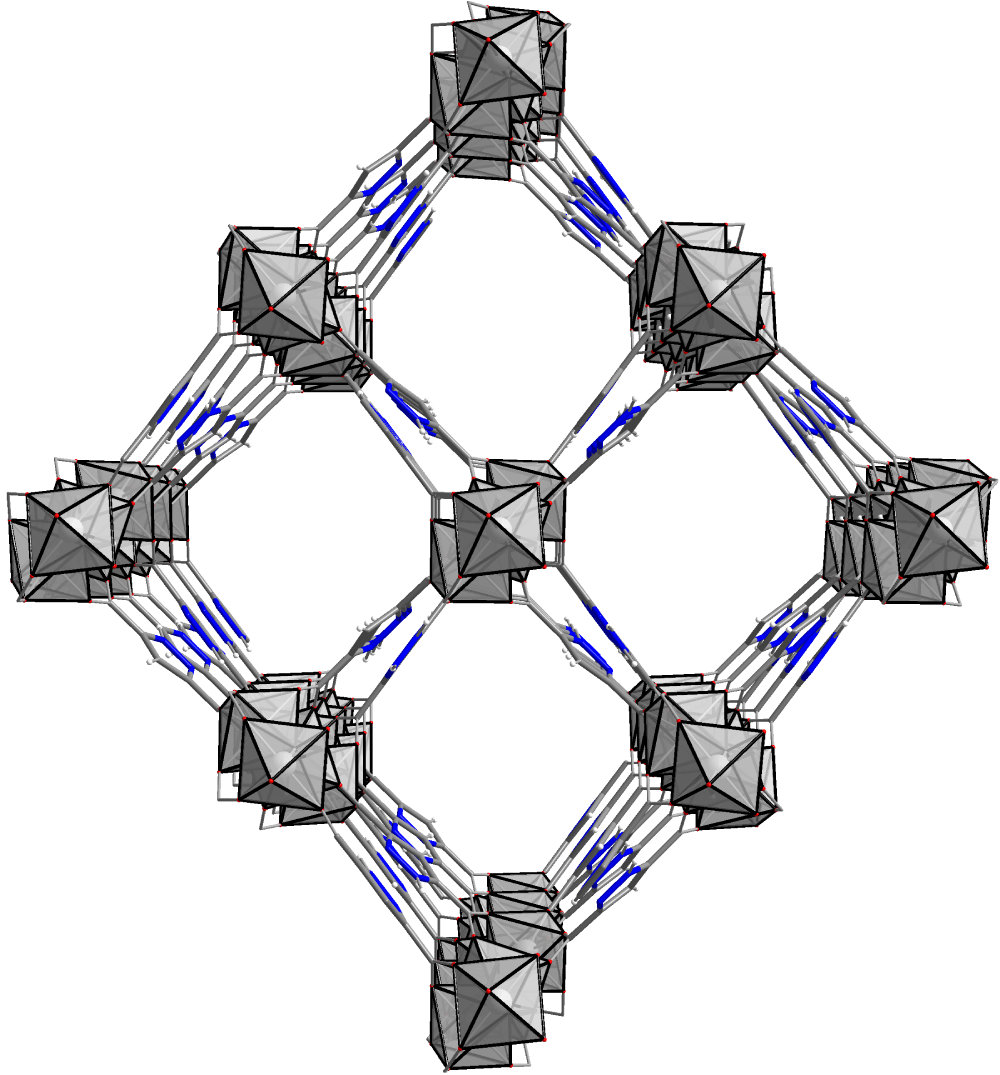
Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are crystalline hybrid materials consisting of metal centers linked by organic molecules forming well-structured frameworks.
MOFs are the fastest-growing class of materials in chemistry today where more than 100 000 MOFs have been found in the last 20 years! Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs), the basis of our technology, were central to the research recognized by the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
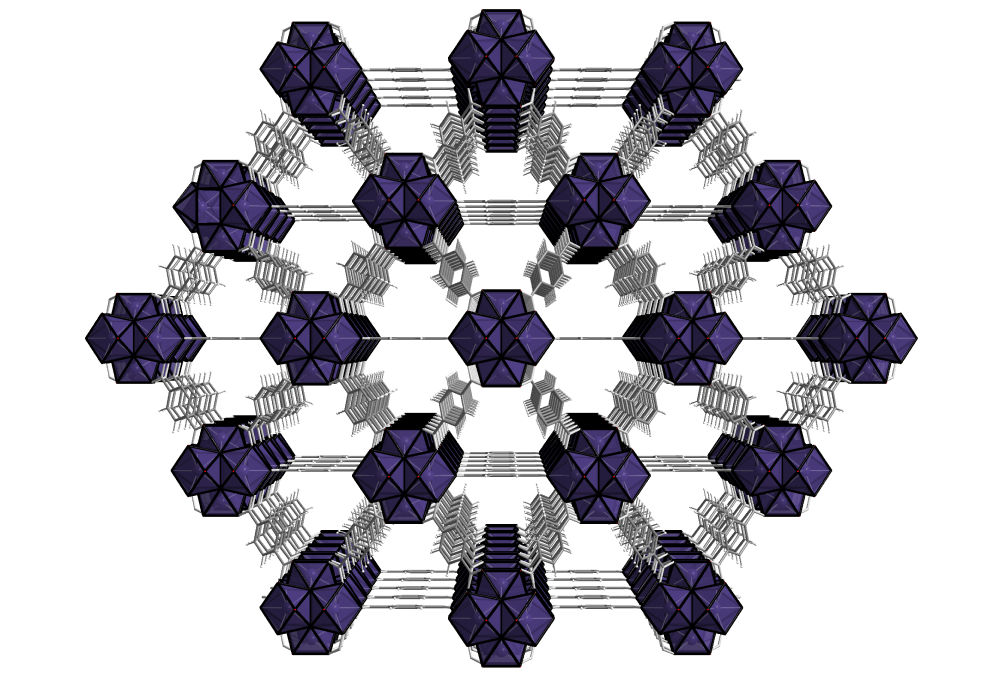
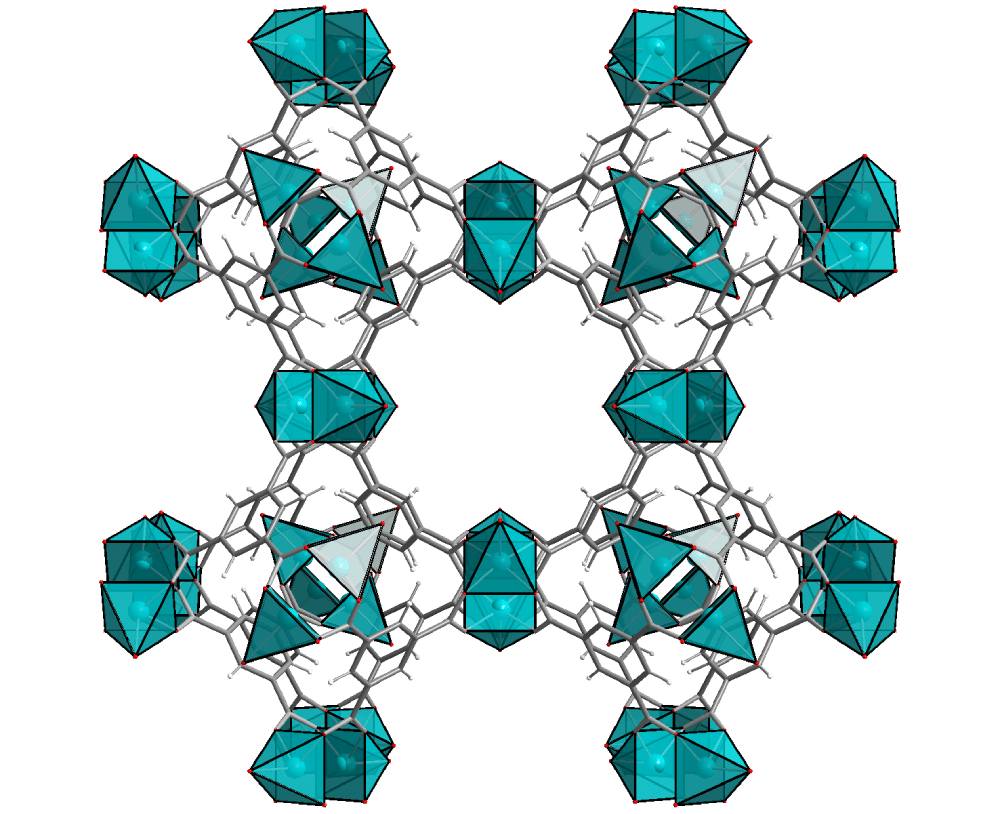
These advanced materials can be compared with sponges. Their porous structure shows unique abilities – taking up, holding, and releasing molecules from their pores by applying different stimuli such as heat, pressure, light, or a magnetic field.

Outstanding surface area
With a highly-ordered framework of pores, metal-organic frameworks exhibit the largest internal surface areas per gram known to man – one gram of MOF can have a surface area comparable to a FIFA soccer field. That is up to 7 000 sqm surface per 1 gram of MOF material.
The large internal surface area offers more space for chemical reactions and adsorption of molecules. But this is not the only reason for the growing engagement of industries and academia toward Metal-Organic Frameworks.
Tunable to your application
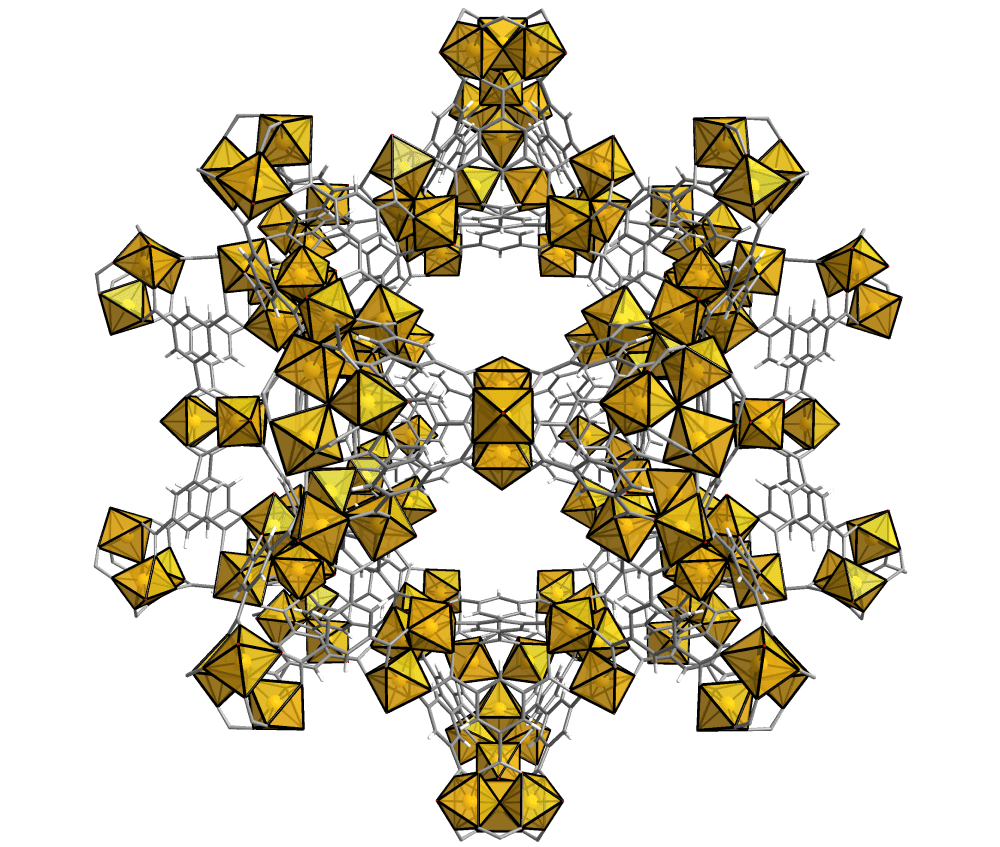
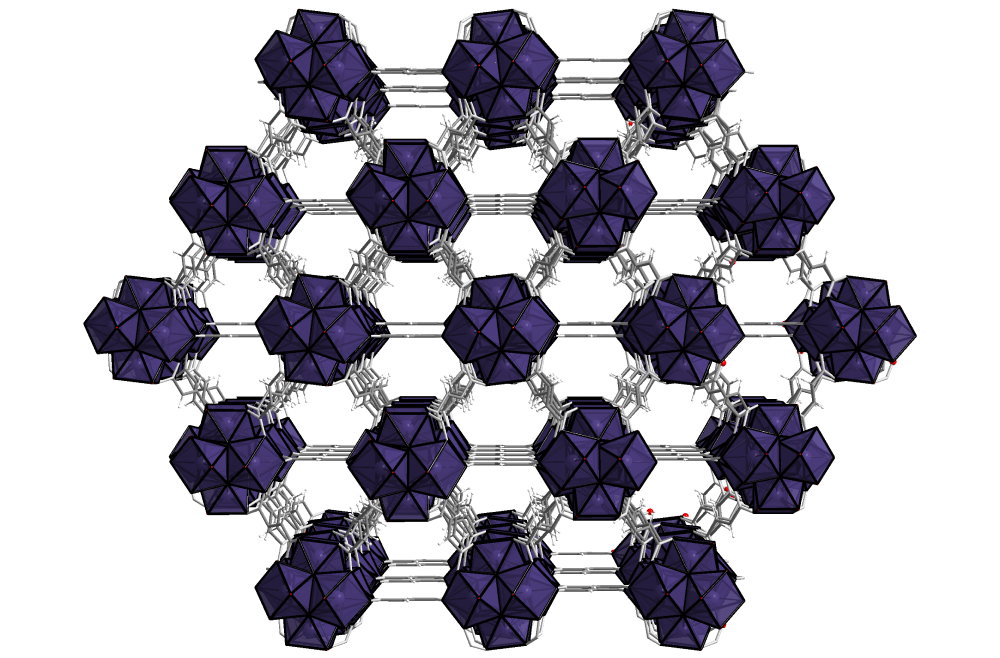
The framework’s building blocks – metal ions and organic linkers – can be combined in almost infinite ways to create novel materials. Nearly every element from the periodic table of elements can be incorporated into the MOF to create novel properties.
Unique structural characteristics can be achieved by tuning the basic materials according to their specified application.
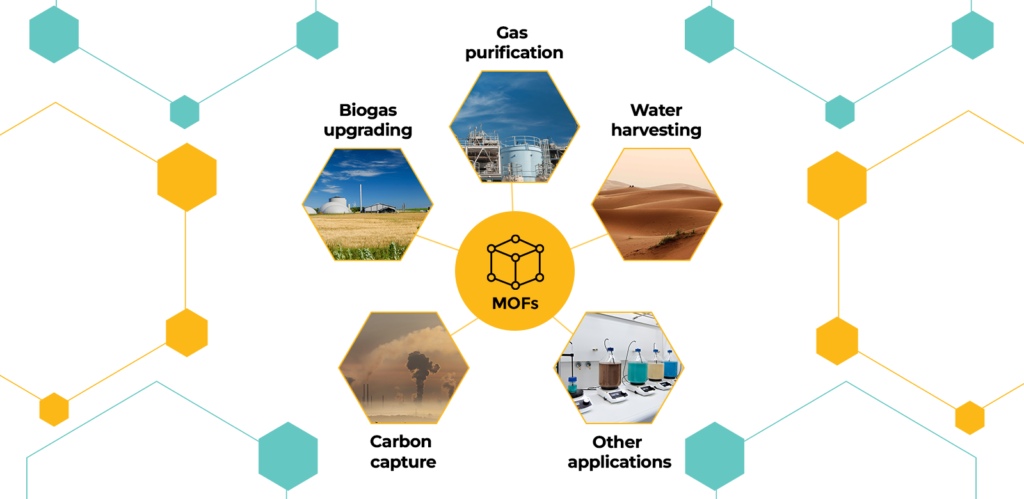
The freedom to choose the elements of the MOF allows for manipulated structures, pore size and shape adjustments, and a wide variety of chemical functionalities offering solutions to various industries and applications. MOFs are a toolbox for current and future problems in processes such as separation, purification, catalysis, gas storage, sensors, and drug delivery.